Acute ischemic stroke (AIS) is a serious medical condition that occurs when blood flow to a part of the brain is blocked by a blood clot. This blockage prevents brain tissue from receiving oxygen and nutrients, leading to cell death if not treated promptly. Thrombolytic therapy, often referred to as “clot busting” treatment, plays a crucial role in managing AIS and improving patient outcomes.
What is ASE Thrombolytic Therapy?
Ase Thrombolytic therapy, specifically using the drug alteplase, is the gold standard treatment for acute ischemic stroke. It involves administering a medication that dissolves the blood clot, restoring blood flow to the affected area of the brain.
Time is of the essence when it comes to stroke treatment. The sooner thrombolytic therapy is administered after the onset of stroke symptoms, the greater the chances of a positive outcome. The established time window for effective treatment is within 4.5 hours of symptom onset, although earlier treatment is always preferred.
How Does ASE Thrombolytic Work?
Alteplase, the medication used in ASE thrombolytic therapy, is a type of tissue plasminogen activator (tPA). It works by binding to fibrin, a protein found in blood clots, and converting plasminogen to plasmin. Plasmin is an enzyme that breaks down fibrin, effectively dissolving the clot and restoring blood flow to the brain.
Benefits of ASE Thrombolytic Therapy
The primary benefit of ASE thrombolytic therapy is its ability to significantly improve the chances of functional recovery after a stroke. By rapidly dissolving the clot, it minimizes the extent of brain damage. Studies have shown that patients who receive timely thrombolytic therapy are more likely to:
- Regain independence in daily activities
- Experience less long-term disability
- Have better cognitive function
- Return to work and social activities
Risks and Considerations
While ASE thrombolytic therapy is a life-saving treatment, it’s important to note that it does come with certain risks. The most significant risk is bleeding, as the medication can increase the likelihood of both internal and external bleeding.
 Potential Risks of ASE Thrombolytic Therapy
Potential Risks of ASE Thrombolytic Therapy
Before administering ASE thrombolytic therapy, healthcare professionals carefully assess patients to determine their eligibility and weigh the potential benefits against the risks.
Eligibility Criteria for ASE Thrombolytic Therapy
Not everyone who experiences an ischemic stroke is eligible for ASE thrombolytic therapy. Strict eligibility criteria have been established to ensure patient safety and maximize treatment effectiveness. Some of the key factors considered include:
- Time Since Symptom Onset: Treatment is most effective within the first 4.5 hours of symptom onset.
- Stroke Severity: Patients with more severe strokes are generally considered good candidates.
- Medical History: Conditions like recent surgery, bleeding disorders, or uncontrolled high blood pressure may preclude treatment.
- Medications: Use of blood thinners or other anticoagulants may affect eligibility.
- Imaging Studies: A CT scan or MRI is essential to confirm the diagnosis of ischemic stroke and rule out hemorrhagic stroke, which is a contraindication for thrombolytic therapy.
The Procedure: What to Expect
If a patient is deemed eligible for ASE thrombolytic therapy, the medication is administered intravenously.
- Assessment: A comprehensive medical history is taken, and a physical examination is performed.
- Imaging: A CT scan or MRI is conducted to confirm the diagnosis and determine the location and extent of the stroke.
- Medication Administration: Alteplase is administered intravenously over a specific timeframe.
- Monitoring: Patients are closely monitored for any signs of complications, such as bleeding or allergic reactions.
- Post-Treatment Care: Following treatment, patients typically remain hospitalized for observation and further management of their stroke.
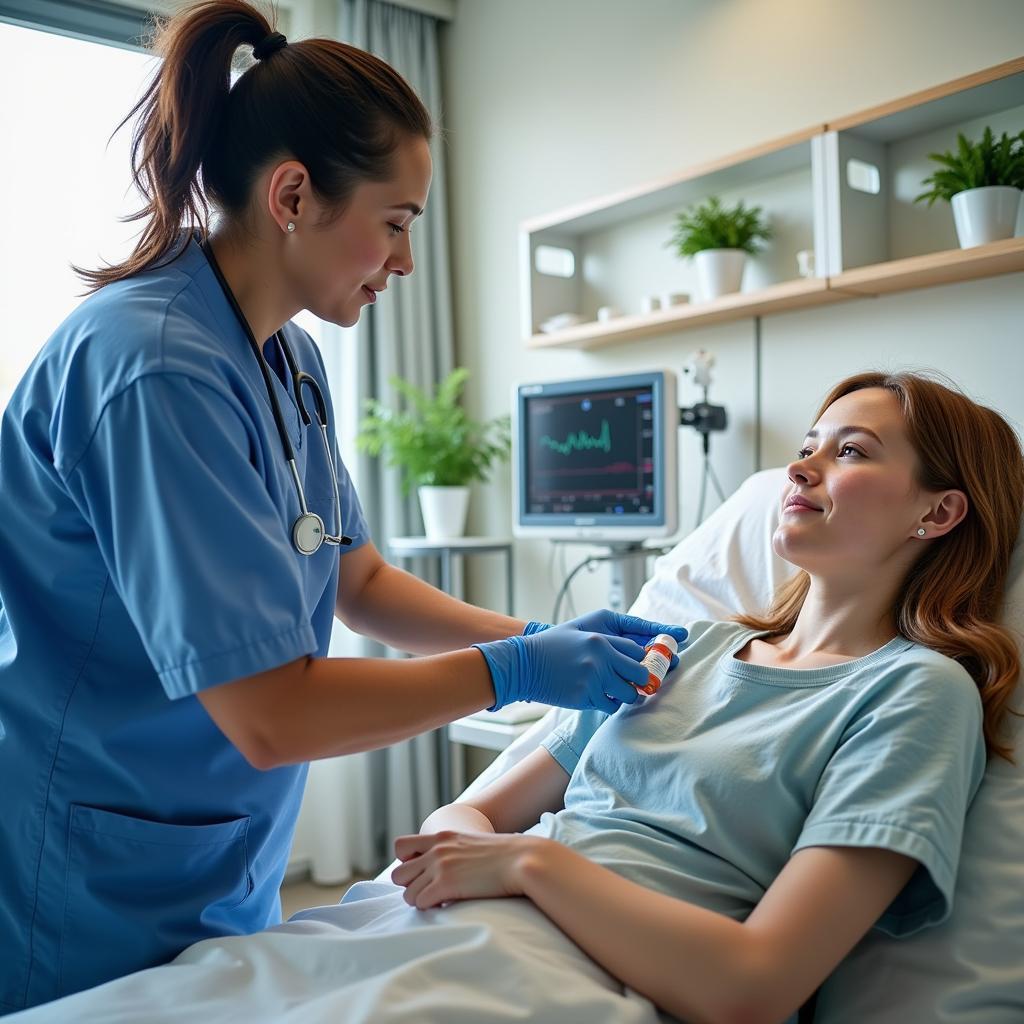 ASE Thrombolytic Administration and Monitoring
ASE Thrombolytic Administration and Monitoring
Long-Term Outlook
The long-term outlook for patients who receive ASE thrombolytic therapy varies depending on several factors, including:
- Time to Treatment: Earlier treatment is associated with better outcomes.
- Stroke Severity: Patients with less severe strokes tend to have a better prognosis.
- Overall Health: Underlying health conditions can impact recovery.
- Rehabilitation: Engaging in rehabilitation therapies, such as physical, occupational, and speech therapy, is crucial for maximizing functional recovery.
Conclusion
ASE thrombolytic therapy, using the medication alteplase, is a cornerstone of acute ischemic stroke treatment. By rapidly dissolving blood clots and restoring blood flow to the brain, this therapy offers patients the best chance of survival and functional recovery. While risks and eligibility criteria must be carefully considered, the potential benefits of ASE thrombolytic therapy in reducing disability and improving quality of life after stroke are significant.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What are the warning signs of a stroke?
2. How long does it take for ASE thrombolytic to work?
3. Are there alternative treatments to ASE thrombolytic therapy?
4. What is the recovery process like after receiving ASE thrombolytic therapy?
5. What lifestyle changes can help prevent future strokes?
Need More Information?
If you have any further questions about ASE thrombolytic therapy or stroke management, please don’t hesitate to reach out to us.
Contact Us:
Phone: 0369020373
Email: [email protected]
Address: Thon Ngoc Lien, Hiep Hoa, Bac Giang, Vietnam
Our dedicated team is available 24/7 to provide support and guidance. For more insights into related topics, explore our other informative articles on ase enzyme meaning.

