Lung compliance, or eAse With Which Lung Tissue Can Be Stretched, is a crucial factor in respiratory health. It determines how easily our lungs inflate and deflate with each breath. Understanding this concept is fundamental to grasping how various respiratory conditions can affect our breathing and overall well-being. This article delves into the complexities of lung compliance, exploring its physiological basis, the factors that influence it, and its significance in diagnosing and managing respiratory diseases.
What Determines Ease with Which Lung Tissue Can Be Stretched?
Several factors contribute to ease with which lung tissue can be stretched, or lung compliance. These include the inherent elasticity of the lung tissue itself, the surface tension within the alveoli (the tiny air sacs in the lungs), and the overall structure of the chest wall and surrounding tissues. Any disruption to these components can significantly impact lung compliance, leading to breathing difficulties.
The Role of Elasticity in Lung Compliance
The elastic properties of lung tissue, primarily determined by elastin and collagen fibers, are essential for normal lung function. These fibers allow the lungs to expand during inhalation and recoil during exhalation, much like a rubber band. When these fibers are damaged or altered, as seen in conditions like emphysema, the lungs lose their elasticity, resulting in increased lung compliance and difficulty exhaling fully.
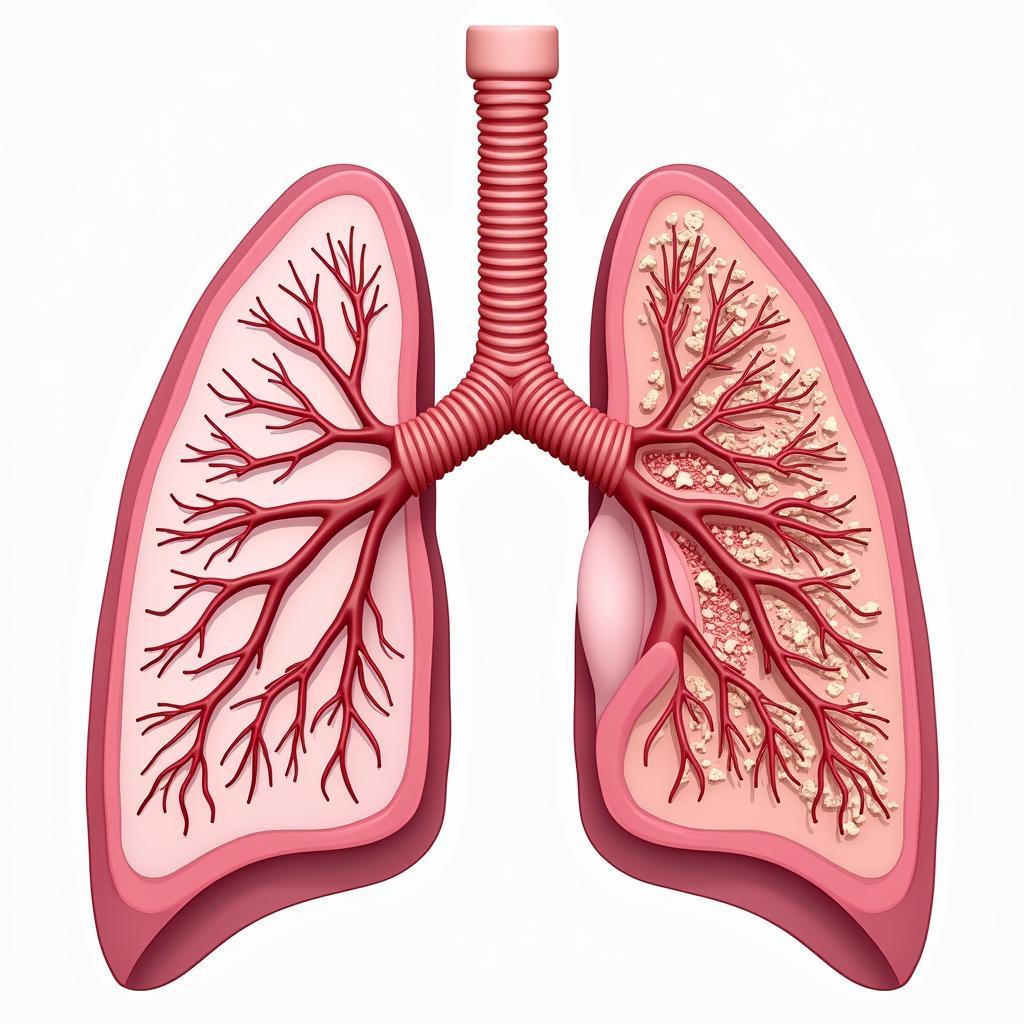 Lung Elasticity and Compliance
Lung Elasticity and Compliance
Surface Tension and its Impact
Surface tension, the force that causes the surface of a liquid to contract, plays a critical role in lung compliance. In the alveoli, a thin layer of fluid lines the inner surface. This surface tension tends to collapse the alveoli, making it harder to inflate them. Fortunately, our bodies produce a substance called surfactant, which reduces surface tension and facilitates lung expansion. Premature babies often lack sufficient surfactant, leading to respiratory distress syndrome.
The Influence of Chest Wall Mechanics
The chest wall and surrounding muscles and tissues also play a role in ease with which lung tissue can be stretched. Conditions affecting the chest wall, such as kyphosis or scoliosis, can restrict lung expansion and decrease lung compliance. Similarly, neuromuscular diseases can weaken the respiratory muscles, making it harder to inflate the lungs.
How is Lung Compliance Measured and Interpreted?
Lung compliance is typically measured using a spirometer, a device that assesses lung function. The measurement involves calculating the change in lung volume for a given change in pressure. A higher lung compliance indicates that the lungs inflate easily, while a lower compliance suggests that the lungs are stiff and difficult to inflate.
The Significance of Lung Compliance in Respiratory Diseases
Changes in lung compliance are a hallmark of various respiratory conditions. Understanding these changes can be crucial in diagnosis and management. For example, increased lung compliance is characteristic of emphysema, while decreased lung compliance is seen in conditions like pulmonary fibrosis and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).
Dr. Amelia Nguyen, a renowned pulmonologist at the National University Hospital in Singapore, explains:
“Lung compliance is a vital parameter in assessing respiratory health. Its measurement helps us differentiate between obstructive and restrictive lung diseases, guiding appropriate treatment strategies.”
Another expert, Dr. Maria Santos, a respiratory therapist at the Lung Center of the Philippines, adds:
“Monitoring lung compliance can be particularly useful in managing patients on mechanical ventilation, allowing us to optimize ventilator settings and minimize lung injury.”
Living with Altered Lung Compliance: Tips and Strategies
Living with altered lung compliance can be challenging, but various strategies can help improve breathing and quality of life. These include pulmonary rehabilitation, breathing exercises, medications, and oxygen therapy.
 Pulmonary Rehabilitation Exercises
Pulmonary Rehabilitation Exercises
Conclusion: The Importance of Understanding Ease with Which Lung Tissue Can Be Stretched
Lung compliance, or ease with which lung tissue can be stretched, is a fundamental aspect of respiratory physiology. Understanding this concept is crucial for recognizing and managing various respiratory conditions. By considering the factors influencing lung compliance and its implications for respiratory health, we can improve diagnosis, treatment, and overall patient outcomes. If you have concerns about your lung health, consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
FAQ
- What is the normal range for lung compliance?
- How does smoking affect lung compliance?
- Can lung compliance improve with treatment?
- What are the symptoms of decreased lung compliance?
- How is lung compliance different from lung capacity?
- What is the role of surfactant in lung compliance?
- How is lung compliance measured in infants?
Related Questions and Articles
- What are the different types of lung diseases?
- How does air pollution impact lung health?
- Understanding the mechanics of breathing.
For further assistance, please contact us at Phone: 0369020373, Email: aseanmediadirectory@gmail.com or visit our office at Thon Ngoc Lien, Hiep Hoa, Bac Giang, Vietnam. Our customer service team is available 24/7.
