Asea Hydroforming is rapidly gaining traction as a cutting-edge manufacturing process in Southeast Asia, revolutionizing how intricate components are shaped and produced. This innovative technique, also known as high-pressure hydroforming, utilizes highly pressurized fluids to mold sheet metal into complex geometries. This article delves into the intricacies of ASEA hydroforming, exploring its applications, advantages, and impact on various industries across the region.
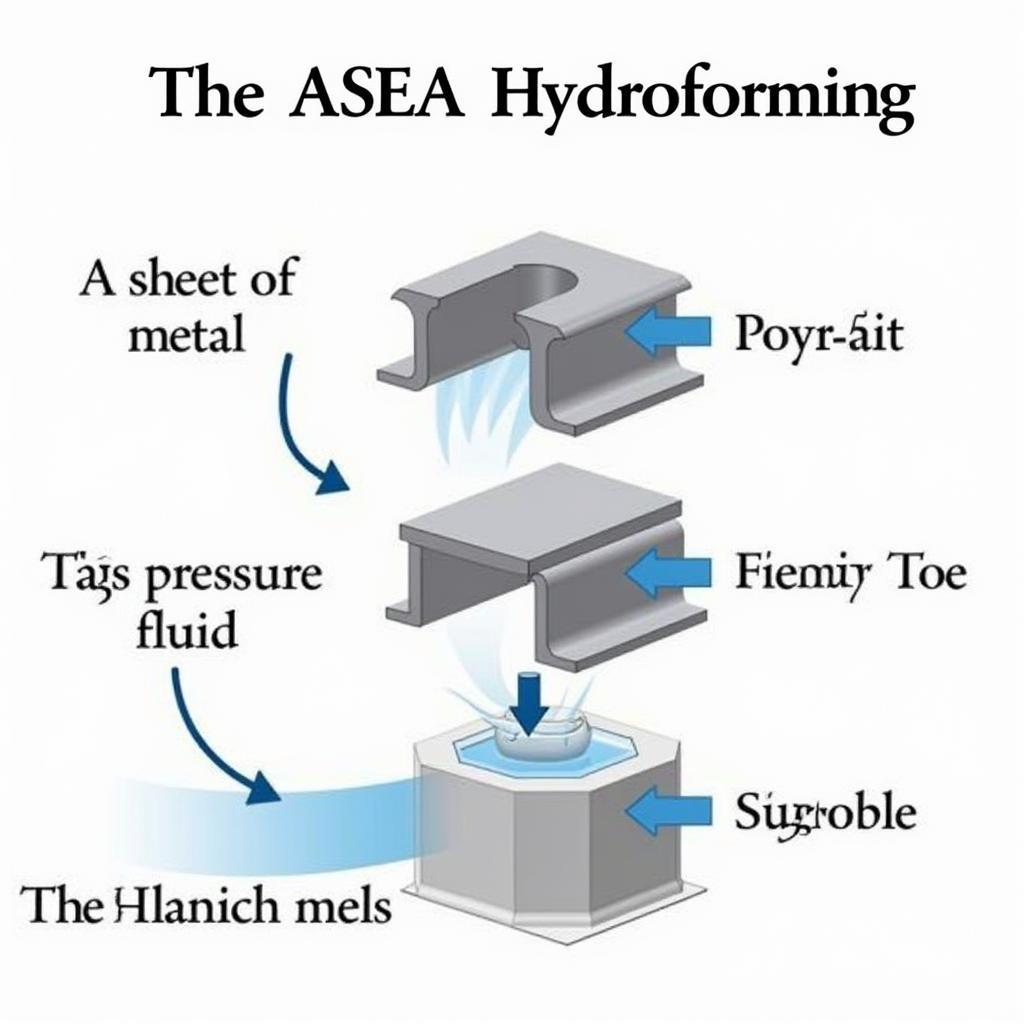 ASEA Hydroforming Process in Action
ASEA Hydroforming Process in Action
Understanding the Mechanics of ASEA Hydroforming
At its core, ASEA hydroforming involves shaping a sheet of metal by subjecting it to controlled, high-pressure fluid within a custom-designed die. This die, which mirrors the desired final shape, acts as a mold. As the fluid pressure increases, it forces the metal to conform to the die’s contours, creating the desired component.
The fluid employed in this process is typically water-based, offering environmental benefits over traditional forming methods that utilize harsh chemicals. The pressure applied can reach an astounding 10,000 psi or more, depending on the material and complexity of the part being formed.
 ASEA Hydroforming in Automotive Manufacturing
ASEA Hydroforming in Automotive Manufacturing
Advantages of ASEA Hydroforming for Modern Manufacturing
The growing popularity of ASEA hydroforming in Southeast Asia stems from its ability to address the increasing demand for complex, lightweight, and high-strength components across various sectors. Let’s delve into the key advantages that make it a game-changer:
- Exceptional Formability: ASEA hydroforming excels in shaping intricate designs with multiple curves and complex geometries. This capability opens doors to innovative product designs that were previously impossible or cost-prohibitive using traditional methods.
- Lightweight Construction: The process allows for the creation of lightweight parts without compromising strength. This is particularly crucial in industries like automotive and aerospace, where reducing weight translates to increased fuel efficiency and improved performance.
- Enhanced Strength and Durability: ASEA hydroformed parts exhibit superior strength-to-weight ratios. The uniform pressure distribution during forming minimizes thin spots and weak points, resulting in components that can withstand high stress and demanding conditions.
- Cost-Effective Production: While the initial setup costs might seem higher, ASEA hydroforming often proves more cost-effective in the long run, especially for large production runs. This is because it reduces the need for secondary operations, simplifies tooling, and minimizes material waste.
Impact on Key Industries in Southeast Asia
The adoption of ASEA hydroforming is transforming manufacturing landscapes across Southeast Asia, making inroads into diverse sectors:
- Automotive: From chassis components and fuel tanks to exhaust systems and structural parts, ASEA hydroforming is pivotal in producing lightweight yet sturdy automotive parts, contributing to improved fuel efficiency and safety.
- Aerospace: The aerospace industry benefits significantly from the ability to create lightweight and incredibly strong components. ASEA hydroforming finds applications in manufacturing engine parts, fuselage sections, and structural components for aircraft.
- Medical Devices: The medical device industry demands precision and biocompatibility. ASEA hydroforming allows for the creation of intricate medical instruments, implants, and devices with complex geometries and smooth finishes.
- Consumer Products: From high-end bicycle frames and sporting goods to intricate designs in electronics and home appliances, ASEA hydroforming expands design possibilities and enhances product durability.
“The precision and flexibility of ASEA hydroforming are unmatched,” states Dr. Nguyen Van Minh, a leading materials scientist in Vietnam. “This technology is empowering Southeast Asian manufacturers to compete globally by producing high-value components for demanding industries.”
The Future Landscape of ASEA Hydroforming
As automation and Industry 4.0 continue to shape manufacturing, ASEA hydroforming is poised for further advancements. The integration of robotics, advanced simulations, and real-time process monitoring will likely lead to even greater precision, efficiency, and material utilization.
ASEA hydroforming is not merely a manufacturing process; it is a catalyst for innovation, enabling the creation of products that were once confined to the realm of imagination. As Southeast Asian nations strive to become global manufacturing hubs, embracing advanced technologies like ASEA hydroforming will be crucial for achieving competitiveness on the world stage.
FAQs about ASEA Hydroforming
1. What are the main materials used in ASEA hydroforming?
While a variety of metals can be used, common materials include aluminum alloys, stainless steel, and high-strength steels.
2. What are the limitations of ASEA hydroforming?
Limitations include the initial investment cost for specialized equipment and the challenge of designing complex dies.
3. Can ASEA hydroforming be used for small-scale production?
While traditionally suited for mass production, advancements in tooling and automation are making ASEA hydroforming increasingly viable for smaller production runs.
For inquiries or support regarding ASEA hydroforming and its applications, contact us at:
Phone Number: 0369020373
Email: [email protected]
Address: Thon Ngoc Lien, Hiep Hoa, Bac Giang, Vietnam
Our dedicated customer support team is available 24/7 to assist you. You may also find related information on asea hydroform and asea fluid forming press on our website.