The Asea Lamprey, a fascinating creature shrouded in mystery, inhabits the freshwater systems of Southeast Asia. While not as well-known as its marine counterparts, this unique species plays a vital role in the region’s aquatic ecosystems.
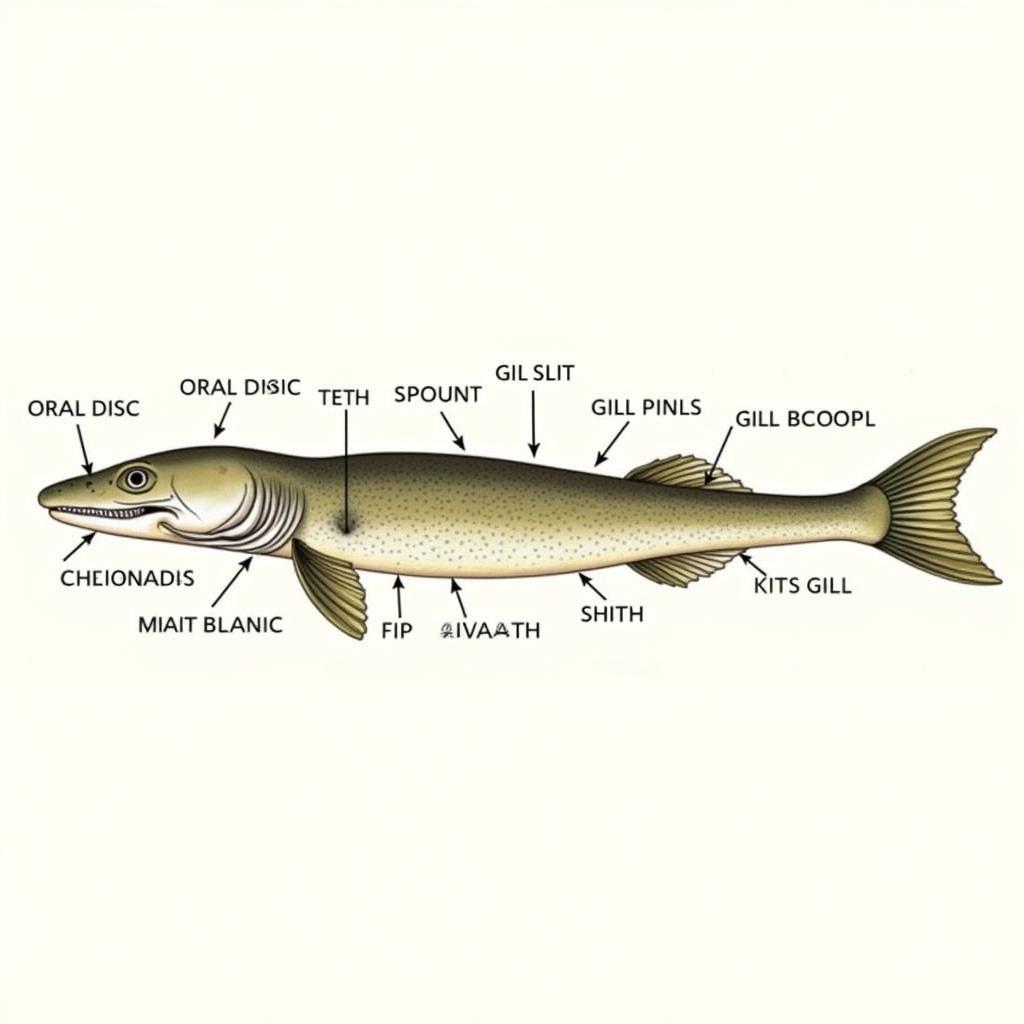 Anatomy of an Asea Lamprey
Anatomy of an Asea Lamprey
Understanding the Asea Lamprey
The Asea lamprey, scientifically known as Lethenteron reissneri, belongs to the family Petromyzontidae. This ancient group of jawless fish has remained relatively unchanged for millions of years, offering a glimpse into the evolutionary history of vertebrates.
Characterized by their elongated, eel-like bodies and lack of scales, lampreys possess a distinctive circular mouth lined with sharp teeth. These teeth are not used for chewing, but rather for attaching to other fish.
Asea lampreys are considered parasitic, meaning they obtain nutrients by attaching to host fish and feeding on their blood and bodily fluids. While this may seem gruesome, it’s important to note that lampreys play a crucial role in regulating fish populations and maintaining the overall health of aquatic ecosystems.
Habitat and Distribution
As their name suggests, Asea lampreys are primarily found in Southeast Asia. Their range extends across various countries, including Thailand, Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia. They prefer freshwater habitats, particularly rivers and streams with clear, flowing water and rocky substrates.
These elusive creatures are often found in areas with moderate to fast currents, as these conditions provide them with ample oxygen and opportunities to encounter suitable host fish. Despite their wide distribution, Asea lampreys are not commonly observed due to their secretive nature and preference for inhabiting deeper waters.
Conservation Status and Threats
The conservation status of the Asea lamprey is currently unknown. Limited research and data availability make it challenging to assess the population trends and potential threats facing this species. However, like many aquatic organisms in Southeast Asia, Asea lampreys are likely facing increasing pressure from human activities.
Habitat loss and degradation, pollution, and climate change pose significant threats to the long-term survival of Asea lampreys. Dam construction and water diversion projects can alter water flow patterns and fragment habitats, making it difficult for lampreys to find suitable spawning grounds. Additionally, pollution from agricultural runoff and industrial discharge can degrade water quality and affect lamprey health.
The Importance of Research and Conservation
Further research is crucial to gain a deeper understanding of the Asea lamprey’s biology, ecology, and conservation needs. By studying this unique species, we can gain valuable insights into the evolution of vertebrates and the intricate relationships that exist within aquatic ecosystems.
Conservation efforts should focus on mitigating the threats facing Asea lampreys and preserving their freshwater habitats. This includes promoting sustainable water management practices, reducing pollution, and raising awareness about the importance of biodiversity conservation.