Overcurrent relays are essential protective devices in power systems, and the Asea Overcurrent Relay stands as a prominent example. These relays detect and interrupt excessive currents, safeguarding equipment from damage caused by faults or overload conditions. This article explores the functionality, types, applications, and benefits of ASEA overcurrent relays, offering a comprehensive guide for engineers, technicians, and anyone interested in power system protection.
ASEA Overcurrent Relay: A Deep Dive
ASEA, a pioneering company in electrical engineering, has a long history of developing reliable and advanced overcurrent relays. These devices are designed to swiftly detect and isolate faults, minimizing downtime and preventing costly equipment failures. ASEA overcurrent relays utilize various technologies, including electromechanical and microprocessor-based designs, to offer a range of protection solutions for diverse power system applications. Understanding the workings of these relays is crucial for ensuring the safety and reliability of electrical networks. 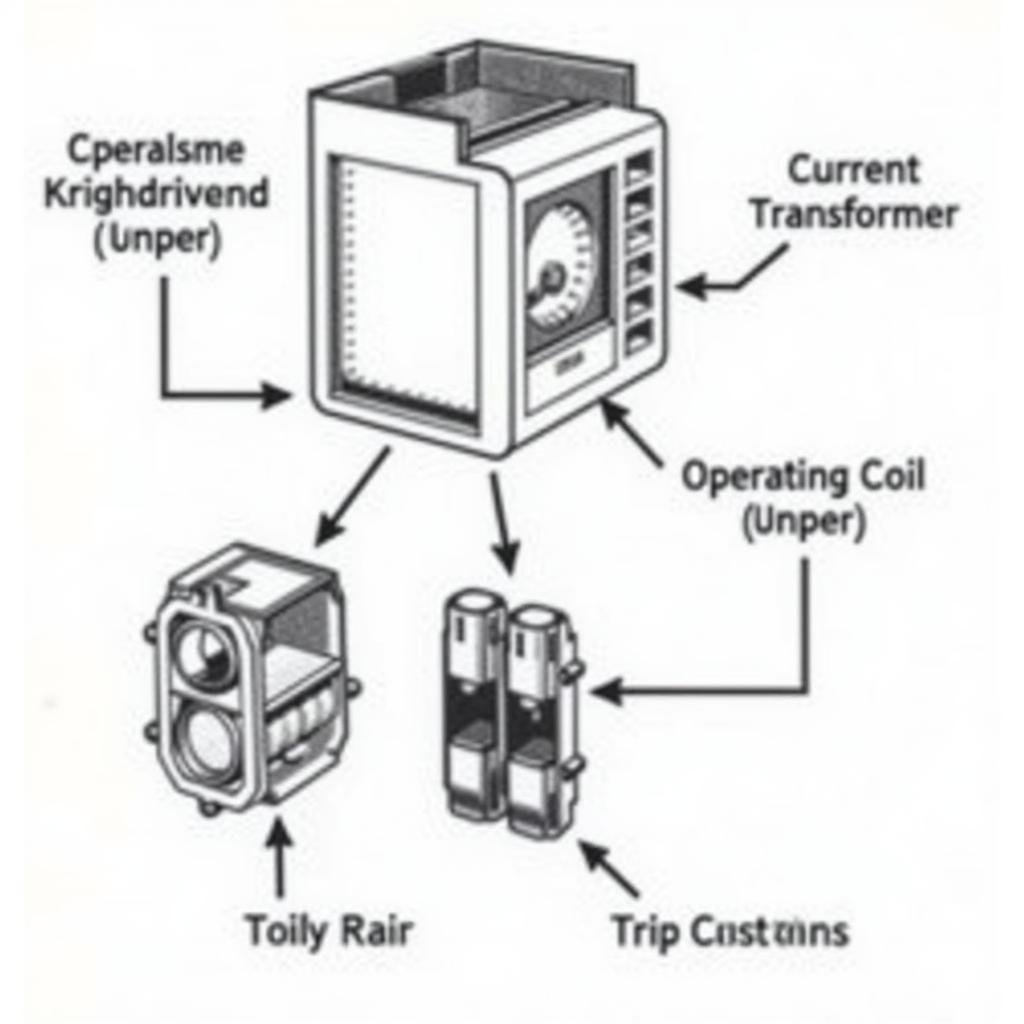 ASEA Overcurrent Relay Basics
ASEA Overcurrent Relay Basics
Types of ASEA Overcurrent Relays
ASEA offers a variety of overcurrent relays tailored to different protection needs. These include:
- Inverse Time Overcurrent Relays: These relays operate with a time delay inversely proportional to the magnitude of the overcurrent. Higher currents result in faster tripping, providing quick protection against severe faults.
- Definite Time Overcurrent Relays: These relays operate with a fixed time delay, regardless of the overcurrent magnitude. They are typically used for backup protection.
- Instantaneous Overcurrent Relays: These relays operate without any intentional time delay, providing rapid protection against very high currents.
Each type has its specific advantages and applications, allowing engineers to select the most suitable relay for the specific protection requirements. asea longitudinal differential protection complements overcurrent protection for critical power lines.
How Does an ASEA Overcurrent Relay Work?
An ASEA overcurrent relay monitors the current flowing through the protected circuit via a current transformer (CT). When the current exceeds a preset threshold, the relay activates, triggering a circuit breaker to interrupt the flow of electricity. This swift action prevents damage to equipment caused by excessive current. 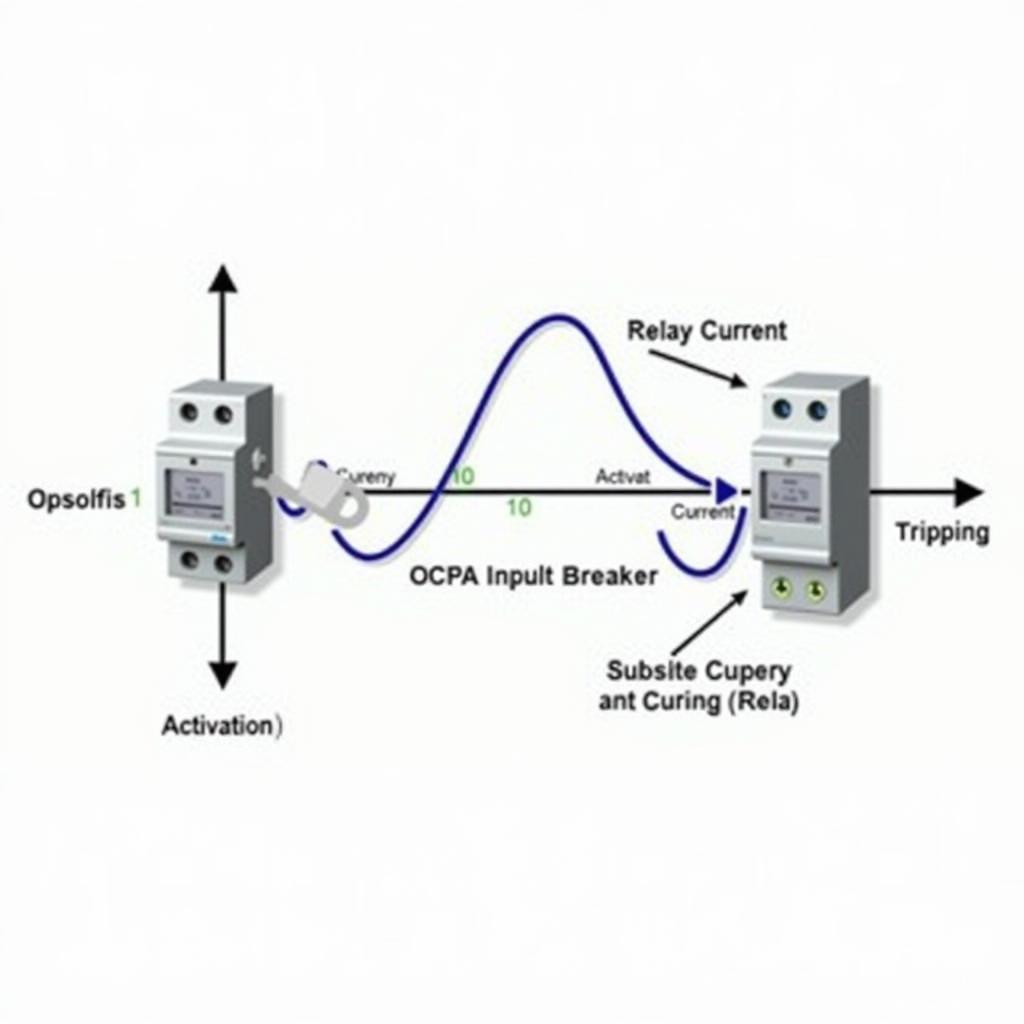 ASEA Overcurrent Relay Operation
ASEA Overcurrent Relay Operation
Applications of ASEA Overcurrent Relays
ASEA overcurrent relays are employed in various power system applications, including:
- Transmission Lines: Protecting against faults and overloads on high-voltage transmission lines.
- Distribution Systems: Safeguarding distribution feeders and transformers from damage.
- Industrial Facilities: Protecting motors, generators, and other critical equipment.
- Renewable Energy Systems: Ensuring the safe and reliable operation of solar and wind power plants.
Benefits of Using ASEA Overcurrent Relays
Using ASEA overcurrent relays provides several key benefits:
- Enhanced Power System Reliability: By swiftly isolating faults, these relays minimize downtime and improve system stability.
- Equipment Protection: Preventing damage to expensive equipment due to overcurrents, saving significant costs.
- Improved Safety: Protecting personnel from electrical hazards by quickly interrupting fault currents.
- Advanced Technology: ASEA overcurrent relays incorporate advanced features, such as microprocessor-based control and communication capabilities, offering enhanced protection and monitoring.
“A robust overcurrent protection scheme, built around reliable relays like those from ASEA, is fundamental to the safety and longevity of any power system,” says Dr. Anya Sharma, a leading power systems engineer at Energy Solutions Inc.
Selecting the Right ASEA Overcurrent Relay
Choosing the appropriate ASEA overcurrent relay requires careful consideration of factors such as:
- System Voltage and Current: Matching the relay’s ratings to the system parameters.
- Fault Current Levels: Ensuring the relay can handle the expected fault currents.
- Protection Requirements: Selecting the appropriate relay type based on the specific application needs.
- Communication Capabilities: Considering the need for remote monitoring and control.
“Proper relay selection is crucial. A mismatched relay can lead to ineffective protection or even nuisance tripping,” adds Mr. Benjamin Nguyen, a senior protection engineer at Power Grid Solutions. asea brown boveri inc s202p is another key component to consider in power systems.
Conclusion
The ASEA overcurrent relay plays a critical role in protecting power systems from the damaging effects of overcurrents. By understanding the various types, applications, and benefits of these relays, engineers can design and implement robust protection schemes that enhance power system reliability, safeguard equipment, and improve overall safety. Choosing the right ASEA overcurrent relay is paramount for effective protection. asea drive contactor is an important component often used in conjunction with overcurrent relays.
FAQ
- What is an ASEA overcurrent relay?
- How does an overcurrent relay work?
- What are the different types of ASEA overcurrent relays?
- What are the applications of overcurrent relays?
- How do I select the right overcurrent relay?
- What are the benefits of using ASEA overcurrent relays?
- Where can I find more information on ASEA overcurrent relays?
Need support? Contact us at Phone: 0369020373, Email: aseanmediadirectory@gmail.com or visit us at Thôn Ngọc Liễn, Hiệp Hòa, Bắc Giang, Việt Nam. We have a 24/7 customer service team.
