The Asean Asian Financial Crisis of 1997-98, often referred to simply as the Asian Financial Crisis, sent shockwaves through the global economy. This period of economic turmoil, triggered by currency devaluations and capital flight, had a profound impact on the ASEAN region, exposing vulnerabilities and prompting significant reforms.
 Impact of the Asian Financial Crisis on ASEAN Economies
Impact of the Asian Financial Crisis on ASEAN Economies
Understanding the Roots of the Crisis
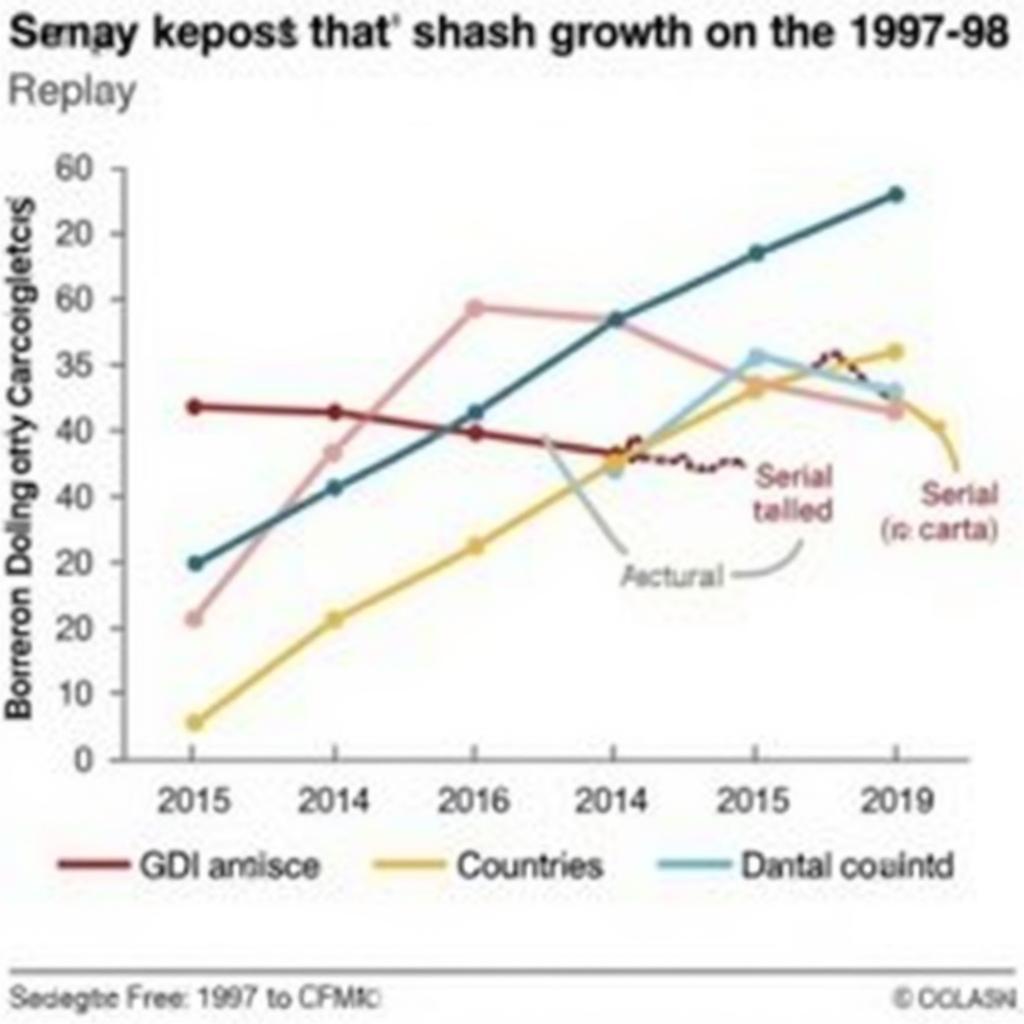
Several factors contributed to the ASEAN Asian Financial Crisis. These included fixed exchange rates, excessive foreign borrowing, weak financial institutions, and cronyism. The crisis began in Thailand with the collapse of the baht and quickly spread to other ASEAN nations like Indonesia, Malaysia, and the Philippines. The rapid outflow of capital led to sharp declines in currency values, stock markets, and asset prices.
The Impact on ASEAN Economies
The crisis had a devastating impact on ASEAN economies. Millions were plunged into poverty, businesses collapsed, and unemployment soared. The social and political consequences were also significant, leading to social unrest and political instability in some countries. The crisis exposed the interconnectedness of ASEAN economies and the vulnerability of the region to global financial shocks.
ASEAN’s Response and Recovery
In the wake of the crisis, ASEAN nations implemented a series of reforms to strengthen their financial systems, improve corporate governance, and promote greater transparency. The ASEAN 3 Framework was established to enhance regional financial cooperation and surveillance. The International Monetary Fund (IMF) also played a crucial role in providing financial assistance and technical support to affected countries. While the recovery was gradual, ASEAN demonstrated resilience and emerged from the crisis with a renewed focus on economic stability and sustainable growth.
Lessons Learned and Long-Term Implications
The ASEAN Asian Financial Crisis provided valuable lessons about the importance of sound macroeconomic policies, strong financial regulation, and regional cooperation. The crisis also highlighted the need for greater transparency and accountability in both the public and private sectors. The ABIF ASEAN and initiatives like the ASEAN AEC Blueprint 2025 are part of the ongoing efforts to build a more resilient and integrated ASEAN economic community.
What triggered the ASEAN Asian Financial Crisis?
Several factors including fixed exchange rates, excessive foreign borrowing, and weak financial institutions contributed to the crisis.
How did the ASEAN Asian Financial Crisis impact the region?
The crisis led to sharp declines in currency values, stock markets, increased poverty, and social unrest.
What were the key lessons learned from the crisis?
The crisis emphasized the importance of sound macroeconomic policies, strong financial regulation, and regional cooperation.
“The Asian Financial Crisis was a wake-up call for ASEAN. It forced us to confront our weaknesses and implement much-needed reforms,” says Dr. Maria Santos, a prominent economist specializing in Southeast Asian economies.
 ASEAN's Future after the Financial Crisis
ASEAN's Future after the Financial Crisis
“The crisis demonstrated the importance of regional solidarity and cooperation in overcoming economic challenges,” adds Professor Lee Wei Ming, an expert on ASEAN economic integration. “The establishment of the ASEAN+3 framework was a crucial step in strengthening regional financial stability.”
Conclusion
The ASEAN Asian Financial Crisis was a watershed moment in the region’s history. While the crisis had a profound and lasting impact, it also served as a catalyst for reform and greater regional cooperation. The lessons learned from the crisis are crucial for ensuring the long-term economic stability and prosperity of ASEAN.
Need support? Contact us 24/7 at Phone Number: 0369020373, Email: aseanmediadirectory@gmail.com, or visit us at: Thôn Ngọc Liễn, Hiệp Hòa, Bắc Giang, Việt Nam.