An Asean Countries Map is an essential tool for understanding the geopolitical landscape of Southeast Asia. It visually represents the ten member states, their locations, and their interconnectedness, offering valuable insights into this dynamic region. This guide will delve into the various aspects of the ASEAN map, its significance, and its implications for regional development.
Decoding the ASEAN Countries Map
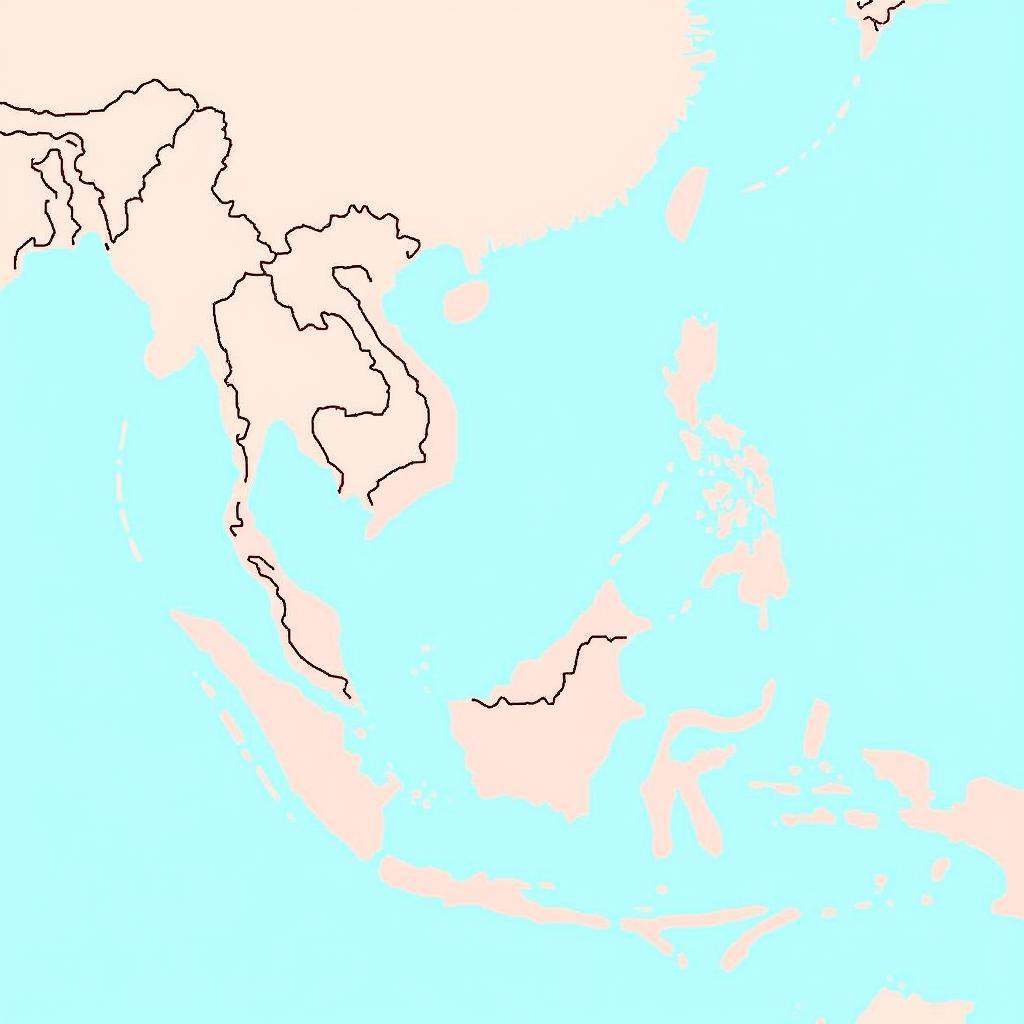 Political Map of ASEAN Countries Showing Borders and Capitals
Political Map of ASEAN Countries Showing Borders and Capitals
The ASEAN countries map depicts a diverse tapestry of nations, each with its own unique history, culture, and political system. From the sprawling archipelago of Indonesia to the bustling city-state of Singapore, the map illustrates the geographical spread and diversity of the region. Understanding the location of each country is crucial for comprehending the complex political and economic dynamics at play. The asean 10 countries map provides a great starting point for this understanding.
Navigating the Geographical Landscape
The map highlights the strategic importance of Southeast Asia, nestled between the Indian and Pacific Oceans. This location has historically made the region a crossroads of trade and cultural exchange, contributing to its rich and multifaceted heritage. Furthermore, the map reveals the diverse topography of the region, from mountainous terrains to fertile river valleys and extensive coastlines. This geographical diversity has shaped the economic activities and livelihoods of the people in each ASEAN country.
The Significance of an ASEAN Countries Map in a Globalized World
In an increasingly interconnected world, the ASEAN countries map serves as more than just a geographical representation. It symbolizes the growing economic and political integration of the region. The ASEAN Economic Community (AEC) aims to create a single market and production base, fostering greater economic cooperation and competitiveness. The map becomes a visual representation of this ambitious project, showing the potential for increased trade, investment, and economic growth. You can find more information on the four pillars of the AEC at 4 pilar utama masyarakat ekonomi asean.
ASEAN’s Role in International Relations
The ASEAN countries map also underscores the region’s growing importance in international relations. ASEAN has become a key player in regional and global forums, advocating for its interests and promoting dialogue and cooperation. The map serves as a reminder of the collective power and influence of the ASEAN bloc in addressing shared challenges, such as climate change, security, and economic development.
“Understanding the geographical context of ASEAN is crucial for comprehending the region’s political and economic landscape. The map provides a visual key to unlocking the complexities of Southeast Asia.” – Dr. Amelia Tan, Southeast Asian Studies expert.
Beyond Borders: ASEAN and its Neighbors
The ASEAN countries map can also be viewed in a broader context, considering the region’s relationship with its neighbors. The map reveals the proximity of major powers like China, India, and Japan, highlighting the importance of maintaining balanced relationships and fostering regional stability. Understanding the geopolitical dynamics at play is essential for navigating the complexities of international relations in the region. More on the relationship with Australia can be found regarding the 2024 asean-australia special summit. Looking at a wider perspective, the asean and gulf countries map highlights burgeoning inter-regional relationships.
A Dynamic Region: Growth and Challenges
Southeast Asia is a region of immense potential, experiencing rapid economic growth and development. However, it also faces significant challenges, such as poverty, inequality, and environmental degradation. The ASEAN countries map provides a framework for understanding these complex issues and working towards sustainable solutions.
“The ASEAN map is a dynamic tool, constantly evolving to reflect the changing realities of the region. It’s a reminder of the interconnectedness of our nations and the importance of working together to achieve common goals.” – Professor Chandra Kumar, Regional Development Specialist.
Conclusion: The ASEAN Countries Map as a Tool for Understanding and Engagement
The ASEAN countries map is a powerful tool for understanding the diverse and dynamic region of Southeast Asia. It provides valuable insights into the geographical, political, and economic landscape, helping us navigate the complexities of this rapidly evolving region. By studying the map and its implications, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead for ASEAN.
FAQ:
- How many countries are in ASEAN? There are ten member states in ASEAN.
- What does ASEAN stand for? ASEAN stands for the Association of Southeast Asian Nations.
- What is the purpose of ASEAN? ASEAN aims to promote regional peace, stability, and economic cooperation.
- Which countries are included in the ASEAN countries map? The map includes Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam.
- Why is the ASEAN countries map important? It provides a visual understanding of the region’s geopolitical landscape and its interconnectedness.
- Where can I find a detailed ASEAN countries map? Several online resources and atlases provide detailed maps of the ASEAN region.
- What is the ASEAN Economic Community (AEC)? The AEC aims to create a single market and production base, fostering greater economic integration.
When you need support, please contact Phone Number: 0369020373, Email: aseanmediadirectory@gmail.com or visit our address: Thon Ngoc Lien, Hiep Hoa, Bac Giang, Vietnam. We have a 24/7 customer service team.